We are Living in The Age of Humans
Earth is changing rapidly, and an increasing number of scientists say that humans have become the dominant force driving these changes. Explore the maps at “We are Living in The Age of Humans” to see an atlas of human influences, as well as the cities that are helping to re-shape the way our species interacts with the planet.
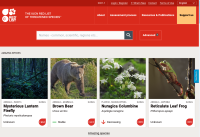
IUCN Red List of Threatened Species
Established in 1964, the International Union for Conservation of Nature’s (IUCN) Red List of Threatened Species has evolved to become the world’s most comprehensive information source on the global extinction risk status of animal, fungus and plant species.
The IUCN Red List is a critical indicator of the health of the world’s biodiversity. Far more than a list of species and their status, it is a powerful tool to inform and catalyze action for biodiversity conservation and policy change, critical to protecting the natural resources we need to survive. It provides information about range, population size, habitat and ecology, use and/or trade, threats, and conservation actions that will help inform necessary conservation decisions. Here you can Learn more about The IUCN Red List
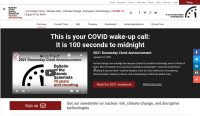
Doomsday Clock
UN report: Nature is going downhill. Fast. (05/15/2019) – from the Bulletin of the Atomic Scientists
According to Wikipedia, the “Doomsday Clock is a symbol that represents the likelihood of a man-made global catastrophe. Maintained since 1947 by the members of the Bulletin of the Atomic Scientists, the clock is a metaphor for threats to humanity from unchecked scientific and technical advances.
The clock represents the hypothetical global catastrophe as midnight and the Bulletin‘s opinion on how close the world is to a global catastrophe as a number of minutes or seconds to midnight, assessed in January of each year. “
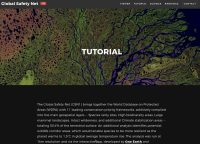
Global Safety Net (GSN1)
The Global Safety Net (GSN1) brings together the World Database on Protected Areas (WDPA) with 11 leading conservation priority frameworks, additively compiled into five main geospatial layers — Species rarity sites, High biodiversity areas, Large mammal landscapes, Intact wilderness, and additional Climate stabilization areas — totaling 50.4% of the terrestrial surface. An additional analysis identifies potential wildlife corridor areas, which would enable species to be more resilient as the planet warms to 1.5°C in global average temperature rise.
The article To save life on Earth, consult this new map gives some background information.
Map of Biodiversity Importance
The Map of Biodiversity Importance is a collaborative effort to identify the places most important for conserving at-risk species. Here is a link to the Living Atlas.The article To save life on Earth, consult this new map gives some background information.
Global Forest Watch
Global Forest Watch dfdf…
Encyclopedia of Life
The Encyclopedia of Life (EOL) is an international effort, led by the Smithsonian Institution’s National Museum of Natural History, to raise awareness and understanding of living nature by providing free, open, multilingual, digital access to trusted information on all known species.
With the help of EOL website search function you can generate a list of species that are extinct in the wild.